Selecting the proper intermediate spacers for hydraulic modular trailers is critical for optimizing load stability, weight distribution, and overall transport efficiency. These spacers help extend trailer length, support heavy loads, and balance axle spacing. Choosing the correct intermediate spacer involves evaluating compatibility with your trailer system, load requirements, and project-specific needs.
This guide outlines the key considerations to help you choose the best intermediate spacers for your modular trailer setup, ensuring safe and efficient transport.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding the Role of Intermediate Spacers
Intermediate spacers are fixed-length components that extend the trailer’s loading area and adjust axle spacing without adding unnecessary load to the axles. These spacers enhance the versatility of modular trailers, enabling them to carry long, oversized, or high-center-of-gravity loads with balanced support.
Key Functions of Intermediate Spacers
- Load Extension: Intermediate spacers increase the trailer’s length to accommodate longer cargo such as pipes, beams, or wind turbine components.
- Weight Distribution: By spacing out the axles, these spacers ensure even weight distribution, which minimizes strain on individual axles and improves the overall stability of the load.
- Fixed Structural Support: They provide stable support for standardized cargo, making them ideal for long, consistent loads.
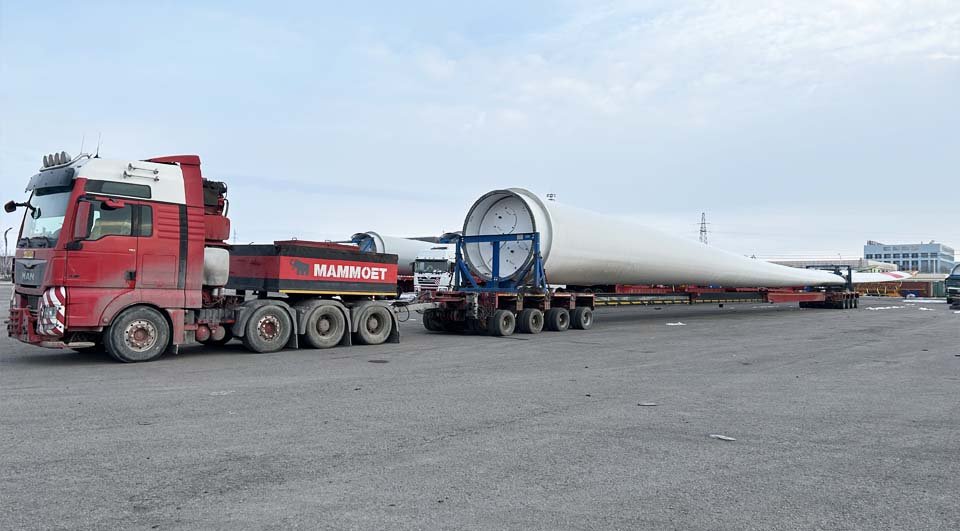

Key Considerations When Choosing Intermediate Spacers
Choosing the right intermediate spacers for your hydraulic modular trailer setup involves considering several factors to ensure they meet your transport needs.
1. Compatibility with Trailer System
- Modular Trailer Model: Make sure the spacers are compatible with your specific modular trailer system. Many spacers are designed to integrate with specific models (e.g., German modules trailer, HPG1 Modualr Trailer) to optimize functionality.
- Axle Configuration: The spacers must align with the trailer’s axle setup to maintain balanced load distribution across the entire trailer.


2. Length Requirements
- Cargo Dimensions: Measure the cargo’s length and choose an intermediate spacer that matches those dimensions. Most spacers range from 3 to 9 meters in length. The spacer length should complement both the cargo and the trailer’s configuration.
- Extended Loading Area: If you’re transporting exceptionally long loads, select spacers that offer enough extension to accommodate the cargo fully, ensuring no overhang or instability.
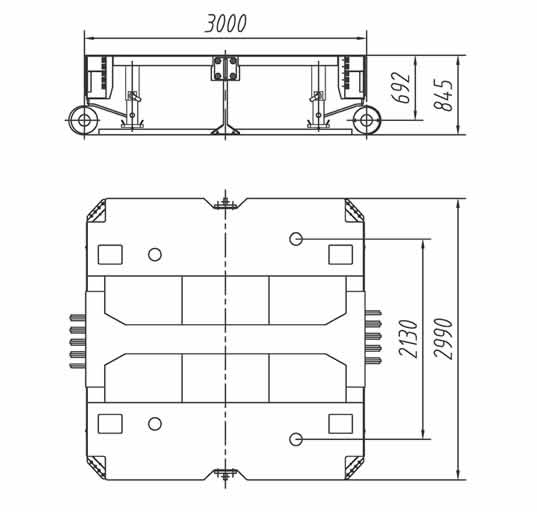
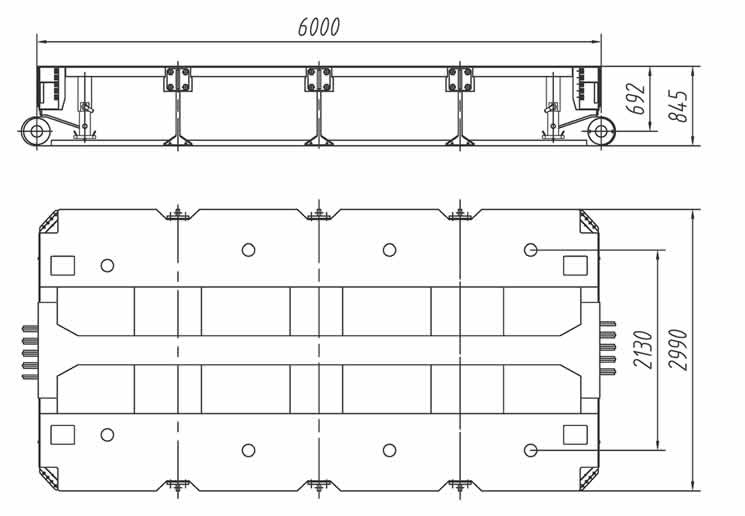
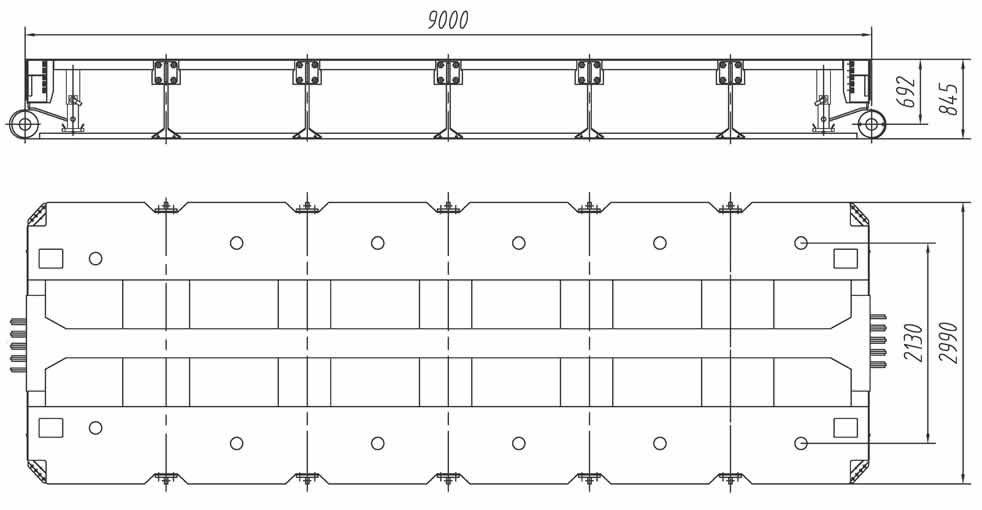
3. Load Capacity
- Weight Distribution: Ensure the spacer can handle the weight distribution requirements for your cargo. Some spacers are designed to support up to 45 tons per axle line, which is crucial for the safe transport of heavy loads.
- Center of Gravity: For loads with a high center of gravity, choose spacers that offer robust support to reduce the risk of tipping, especially with long and narrow cargo.
4. Material and Construction
- High-Strength Materials: Opt for spacers made from durable materials like Q690 high-tensile steel, known for its strength and resistance to bending moments and concentrated loads.
- Reinforced Frame: The spacer frame should have a box-shaped structure with cross beams and outer beams, ensuring structural integrity similar to that of the trailer bogies.
- Integrated Systems: Look for spacers with built-in hydraulic, braking, and electrical systems, ensuring efficient operation and seamless connectivity between trailer modules.
5. Specific Applications
- Industry-Specific Use: Understand the specific applications where the spacers will be used. For example, intermediate spacers are highly beneficial in wind power projects or for transporting long and light loads, where consistent load distribution is critical.
- Project Demands: Consider if the spacer will be used for standardized cargo (e.g., beams, pipelines) or specialized loads with unique dimensions, and choose accordingly.
6. Operational Flexibility
- Fixed-Length vs. Extendable Options: Decide whether fixed-length intermediate spacers will suffice, or if you require extendable spacers for flexibility. Extendable spacers offer more adaptability for on-site adjustments but tend to be more complex and costly.
- Efficiency and Ease of Use: Fixed-length spacers are generally quicker and easier to set up, making them ideal for consistent load requirements. However, extendable spacers provide flexibility for projects with varying load sizes.
7. Cost and Budget
- Cost-Effective Solutions: Consider your budget and the features needed for the project. Fixed-length spacers are generally more budget-friendly because of their simpler construction.
- Long-Term Investment: Although extendable spacers are more expensive, they offer greater versatility and could be advantageous for operations that frequently handle various types and sizes of cargo.
Types of Intermediate Spacers and Their Applications
Understanding the different types of intermediate spacers helps you choose the right one for your specific needs.
1. Fixed-Length Intermediate Spacers
- Description: These spacers provide a set increase in trailer length and offer stable support without adjustability.
- Applications: Fixed-length spacers are perfect for transporting consistent loads such as beams, pipelines, or prefabricated sections.
- Advantages: They are cost-effective and durable, making them efficient for projects with predictable load requirements.
2. Telescoping (Extendable) Intermediate Spacers
- Description: Extendable spacers can be adjusted in length, allowing operators to match the spacer length with the cargo’s size.
- Applications: Ideal for projects with varying load sizes, such as construction materials or modular machinery.
- Advantages: They provide on-site flexibility, enabling quick adjustments to suit different cargo dimensions.
3. Heavy-Duty Intermediate Spacers
- Description: These spacers are designed with reinforced frames to support high-capacity loads and provide extra stability for extremely heavy cargo.
- Applications: Used for industrial transport, especially for oversized machinery or construction materials.
- Advantages: These spacers are essential for handling exceptionally heavy loads safely and efficiently.
Best Practices for Using Intermediate Spacers
To maximize the performance and safety of your intermediate spacers, follow these best practices:
- Conduct Pre-Trip Inspections: Ensure that all connections, hydraulic systems, and load alignments are secure before setting out. Check for any signs of wear or damage on the spacers.
- Balance Load Distribution: Position the load carefully to maintain even weight distribution across all axles, especially for high-center-of-gravity loads.
- Route Planning: Account for any route limitations, such as clearance requirements or road width restrictions. Ensure the spacer length complies with height or width limits along the route.
- Operator Training: Proper training ensures that operators know how to handle intermediate spacers safely and effectively, particularly when balancing loads and securing cargo.
Summary: Choosing the Right Intermediate Spacer for Your Modular Trailer
The appropriate intermediate spacer is key to ensuring safe, efficient, and cost-effective transport. By considering factors like compatibility, load capacity, material strength, and operational flexibility, you can choose the spacer that best meets the specific needs of your project.
Key Takeaways
- Compatibility: Verify that the spacer matches your modular trailer model and axle setup.
- Length and Load Capacity: Select spacers that provide the right length and can support the weight distribution of your cargo.
- Material Strength: Opt for spacers made from high-strength materials like S690 steel for durability.
- Flexibility: Assess whether fixed-length or extendable spacers are more suitable based on cargo variability and project demands.
With the right intermediate spacer, your hydraulic modular trailer setup will be equipped to handle even the most demanding heavy-haul projects, optimizing safety, performance, and efficiency.
For more detailed guidance or to explore different types of intermediate spacers and their applications, visit Hydraulic Modular Trailer Accessories.
